In 2024, the Eurozone is navigating through a landscape marked by economic challenges, from inflationary pressures to geopolitical tensions. Yet, the resilience of its member states has been evident, showcasing an ability to adapt and thrive amidst uncertainty. This article delves into the various factors that contribute to the Eurozone’s resilience, the challenges it faces, and the strategic measures being implemented to ensure stability and growth.
Understanding the Eurozone Economy
The Eurozone, comprising 19 of the 27 European Union (EU) member states, uses the euro as its official currency. This unique monetary union has its own central bank, the European Central Bank (ECB), which plays a pivotal role in managing monetary policy across the region. The Eurozone is one of the world’s largest economies, with a GDP of approximately €14 trillion. Its significance is not only economic but also geopolitical, as it serves as a model for regional cooperation.
The Impact of Global Events on the Eurozone
The Eurozone has faced a series of global challenges over the past few years. The COVID-19 pandemic wreaked havoc on economies worldwide, leading to unprecedented fiscal responses. The invasion of Ukraine by Russia in 2022 further complicated the situation, leading to soaring energy prices and supply chain disruptions. These events have resulted in inflation rates that have spiked across the Eurozone, putting pressure on households and businesses alike.
Inflation: A Persistent Challenge
In 2024, inflation remains a critical issue for the Eurozone. After peaking at record levels in 2022 and 2023, inflation rates have started to show signs of stabilization, but remain above the ECB’s target of 2%. The primary drivers of inflation include:
- Energy Prices: High energy costs, exacerbated by the ongoing geopolitical tensions, have significantly contributed to overall inflation. Although energy prices have stabilized somewhat, they remain volatile and can impact the economy quickly.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Continued disruptions in global supply chains have affected the availability of goods, leading to higher prices. The pandemic’s long-term effects are still being felt, complicating recovery efforts.
- Wage Growth: As inflation pressures persist, wages are rising in response, creating a cycle that can perpetuate inflation if not managed carefully.
ECB’s Response to Inflation
The European Central Bank has been proactive in combating inflation through a series of interest rate hikes. In early 2024, the ECB raised its benchmark interest rate for the sixth consecutive time, bringing it to 4%. This aggressive approach aims to curtail inflation by making borrowing more expensive, thus slowing consumer spending and investment.
However, this approach has its risks. Higher interest rates can slow down economic growth, potentially leading to a recession. The challenge for the ECB is to strike a balance between controlling inflation and ensuring economic growth. The bank is closely monitoring economic indicators and may adjust its policies as necessary.
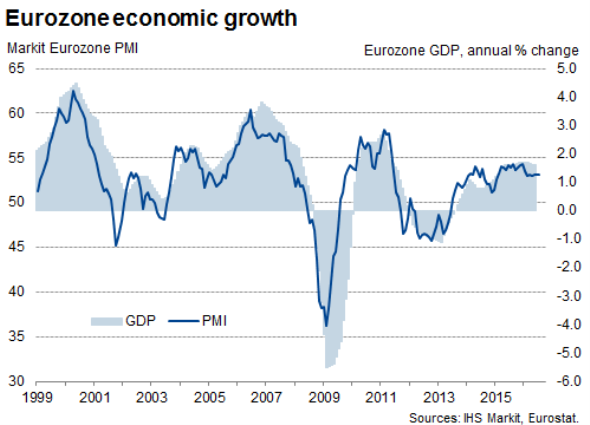
Economic Growth: A Mixed Outlook
Despite the challenges, there are signs of resilience and recovery within the Eurozone. Several factors contribute to a mixed but optimistic outlook for economic growth in 2024.
Strong Labor Markets
The labor market in many Eurozone countries has shown remarkable resilience. Unemployment rates have remained relatively low, hovering around 6.5% across the region. Countries like Germany, the largest economy in the Eurozone, have managed to maintain low unemployment rates due to robust job creation and a strong export sector.
This resilience in the labor market provides consumers with purchasing power, which is crucial for economic growth. However, disparities exist between member states, with southern European countries like Spain and Italy facing higher unemployment rates, impacting their economic recovery.
Increased Consumer Confidence
Consumer confidence is gradually returning, buoyed by improved labor market conditions and government support programs. In 2024, many households are seeing increased disposable incomes, which is helping to fuel domestic demand. The EU’s Next Generation EU recovery fund, designed to support economic recovery, has also provided much-needed financial assistance to member states.
Investments in Green and Digital Transitions
The Eurozone is also making significant strides in transitioning to a greener economy. The European Green Deal, an ambitious plan to make Europe the first climate-neutral continent by 2050, is driving investments in renewable energy and sustainable practices. In 2024, member states are channeling funds into green technologies, which not only help combat climate change but also create jobs and stimulate economic growth.
Digital transformation is another key area of focus. The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital technologies across various sectors, and this trend continues in 2024. Investments in digital infrastructure, e-commerce, and digital skills are paving the way for future growth.
Geopolitical Challenges and Their Economic Implications
The Eurozone’s economic stability is not only challenged by internal factors but also by external geopolitical tensions. The ongoing war in Ukraine has far-reaching implications for Europe, including:
- Energy Security: The reliance on imported fossil fuels has made the Eurozone vulnerable to price shocks. Efforts to diversify energy sources and invest in renewables are underway, but the transition will take time.
- Trade Relations: Sanctions imposed on Russia have disrupted trade relations, impacting several sectors, including agriculture and manufacturing. The Eurozone must adapt to new trade dynamics and seek alternative markets.
- Migration Pressures: Geopolitical instability can lead to increased migration, posing challenges for social integration and public services in host countries. The Eurozone must balance humanitarian responsibilities with economic realities.
Conclusion: Building Resilience for the Future
As the Eurozone navigates through economic challenges in 2024, its resilience is evident through a combination of strong labor markets, strategic investments, and proactive monetary policies. While inflation and geopolitical tensions present significant hurdles, the commitment to innovation, sustainability, and economic cooperation among member states offers a pathway toward stability and growth.
Looking ahead, the Eurozone’s ability to weather these challenges will depend on the collective efforts of its member states and institutions. By fostering resilience and adaptability, the Eurozone can continue to thrive in an increasingly complex global landscape, positioning itself as a model of economic cooperation and sustainability for the future.

